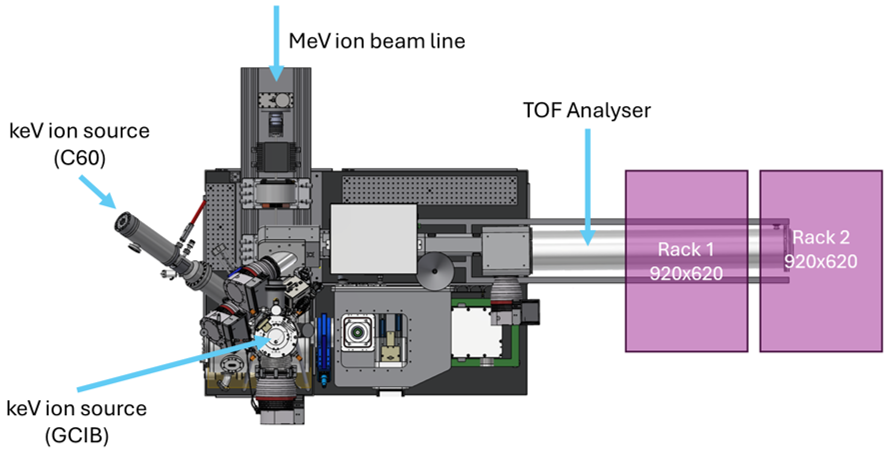
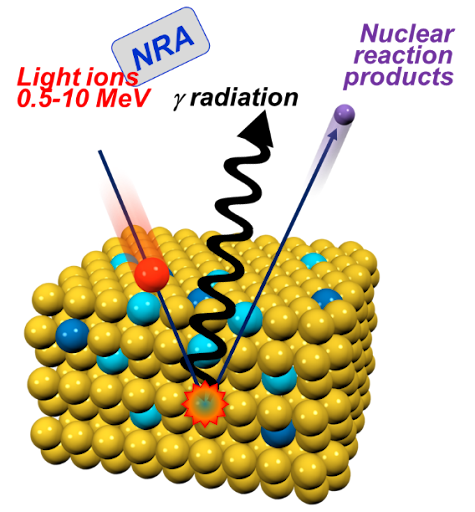
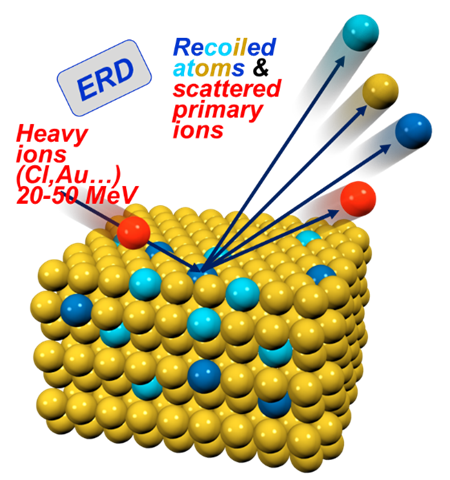
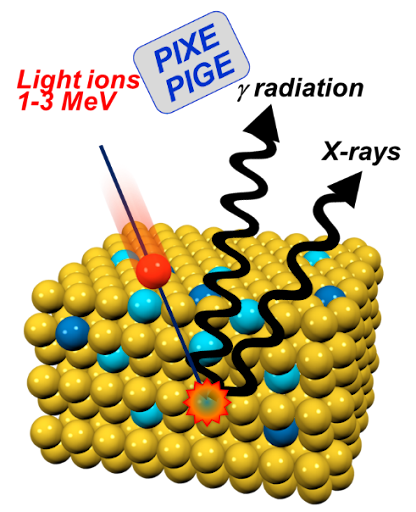
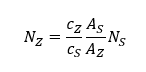Time-of-Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (TOF-ERDA) is an ion-beam analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition and depth profiles of materials, particularly light elements like hydrogen. It works by directing a high-energy ion beam—often heavy ions such as iodine or chlorine—onto a sample surface, causing atoms to recoil out of the material. The recoiled atoms are detected, and their time of flight is measured to determine their mass and energy. This combination enables precise identification of elements and accurate depth-resolved quantification. TOF-ERDA offers excellent sensitivity to light elements, which many other analytical methods struggle to resolve. It provides near-surface to micrometer-scale depth profiling with high resolution. Because it measures energy and time independently, it reduces ambiguities in mass separation.
Research Areas

 Research Areas
Research Areas
The Surrey Ion Beam Centre (SIBC) showcases a diverse portfolio of case
studies that highlight how its advanced ion beam facilities support innovation
across academia, industry, and interdisciplinary research. These examples
demonstrate the Centre’s ability to apply ion implantation, irradiation, and ion
beam analysis techniques to solve real-world scientific and engineering
challenges.
From semiconductor device development and quantum technology fabrication
to radiation-damage testing, heritage science, materials characterisation, and
biomedical research, the case studies illustrate the versatility and impact of ion
beam methods. Each project reflects SIBC’s collaborative approach, combining
specialist technical expertise, state-of-the-art instrumentation, and tailored
support for users at all levels of experience.
Together, these case studies provide a practical insight into how the SIBC
translates complex ion beam capabilities into measurable outcomes -
accelerating research, supporting industrial innovation, and enabling
breakthroughs across multiple scientific domains.
-
 Metalloprotein Analysis
Metalloprotein Analysis
-
 Multimodal Imaging
Multimodal Imaging
-
 ToF – ERDA
ToF – ERDA
-
 RBS
RBS
Metallo Protein Analysis
Metallo-protein analysis focuses on studying proteins that contain metal ions as part of their structure. It identifies the type and amount of metal present and examines how the metal interacts with the protein. Techniques like UV–Vis spectroscopy, ICP-MS, X-ray crystallography, and EPR help characterize metal centers. This analysis reveals the metal’s role in catalysis, electron transfer, stability, and protein activity.
It also helps understand oxidation states, metal-binding sites, and coordination geometry. Metallo-protein analysis is crucial because nearly one-third of all proteins depend on metals. It aids in identifying how disruptions in metal binding can lead to diseases.
Ion Beam Analysis of Metals in Proteins
Geoffrey W. Grime


📰
Geoffrey W. Grime et al. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2020 142 (1), 185-197.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b09186
Why measure metals in proteins?
- Proteins are basic components of biochemical processes including cell function, tissue building, disease processes and metal transport (e.g. haemoglobin).
- Proteins are linear chains of amino acids folded into complex 3D shapes. Shape determines function.
- Many proteins contain small numbers of metal atoms. X-ray crystallography is routinely used to determine the position of each non-hydrogen atom in a protein, including metals. However, this relies on fitting the electron density, which does not allow the unambiguous identification of the metal.
- Micro particle induced X-ray emission (µPIXE) can identify and quantify unknown metal atoms in proteins.
The scale of the problem
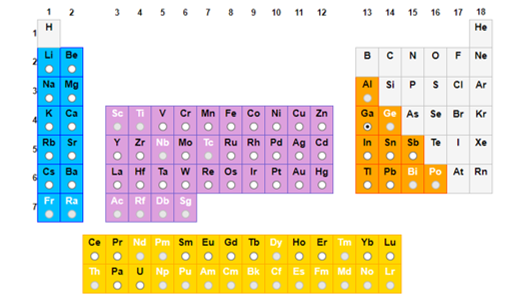
- ☐ Over one third of all proteins with known 3-D structure are identified as containing metal atoms or binding sites.
- ☐ Elements with round white symbols have been identified in a protein structure.
Our work indicates that up to 30% of metal assignments may be incorrect, possibly leading to erroneous biological conclusions being drawn from the structures.
Analysis of metals in proteins using PIXE
☐ Absolute measurement of metal concentration is not easy
☐ Metal concentrations are low
☐ Proteins must be dissolved in buffer solutions so amount of protein may not be well known
The scale of the problem
Elspeth’s insight in 1993:
c is measured concentration
A is atomic weight
N is the number of detected metal atoms of interest per molecule
Z, S refer to the metal atom of interest and sulphur
☐ Using ratios eliminates many sources of error affecting absolute measurement.
☐ Other elements may be used as the reference (e.g. P in nucleic acids, Se following seleno-methionine substitution.)

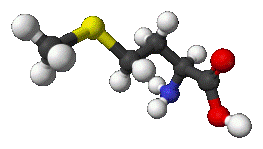
Methionine molecule
Ion Beam Analysis of Metals in Proteins
Geoffrey W. Grime


📰
Examples
Human Insulin: The importance of Zinc (Zn)
Diabetics who inject insulin may suffer from amyloidosis, an inflammation at the injection site.
- Caused by insulin aggregating to form fibrils and spherulites that compromise its action.
- PIXE showed that zinc is expelled on aggregation of insulin.
- PIXE was crucial for the study and this finding is helping develop treatments for amyloidosis.


Ion Beam Analysis of Metals in Proteins
Geoffrey W. Grime


📰
R.J. Ragotte et al. Nat Commun 13, 933 (2022). DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28601-4
Examples
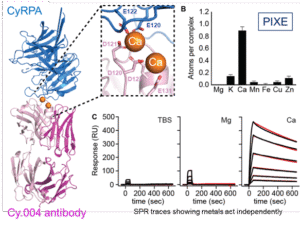
Malaria vaccines: do our antibodies help each other?
Need to understand mechanism of synergy of antibodies against malaria to improve vaccine design. Calcium appears vital for maximum response.
- CyRPA is a protein of the malaria parasite.
- A panel of antibodies that bind to CyRPA and strongly inhibit parasite growth in vitro (Cy.00x) were tested and their 3-D structures found.
- PIXE used to identify and quantify metals and confirmed that calcium was vital to the binding.


Ion Beam Analysis of Metals in Proteins
Geoffrey W. Grime


📰
Shee Chien Yong et al. Science 345,1170 1173 (2014).
DOI: 10.1126/science.1254237
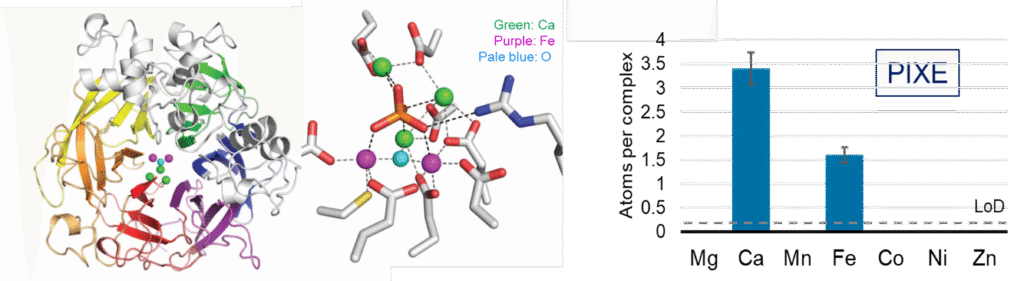
Examples
P. fluorescens PhoX alkaline phosphatase
Uptake of phosphate by micro-organisms is mediated by phosphatases such as PhoX
- PhoX contains an active-site cofactor with 5 metal binding sites .
- PIXE indicated 3 Ca ions and 2 Fe ions.
- No other candidate metals (Mg, Mn, Co, Ni, Zn) were detected.
The presence of iron in PhoX raises the possibility that microbial phosphate acquisition is limited by iron bio-availability.
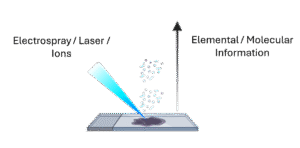
Multimodal Imaging
Multimodal imaging in Ion Beam Analysis is a comprehensive approach that integrates several complementary ion-based techniques to provide a richer understanding of a sample’s structure and composition. By combining methods such as PIXE for sensitive elemental mapping, RBS for depth-resolved composition, ERDA for detecting light elements including hydrogen, and STIM for high-resolution structural or density imaging, researchers can correlate chemical, spatial, and structural information that no single technique can provide on its own. This integrated workflow reduces ambiguity, strengthens quantification, and enables precise localization of elements within complex microstructures while remaining largely non-destructive.
Multimodal Imaging: Elements & Molecules in Biological Samples
Catia Costa & Melanie J. Bailey



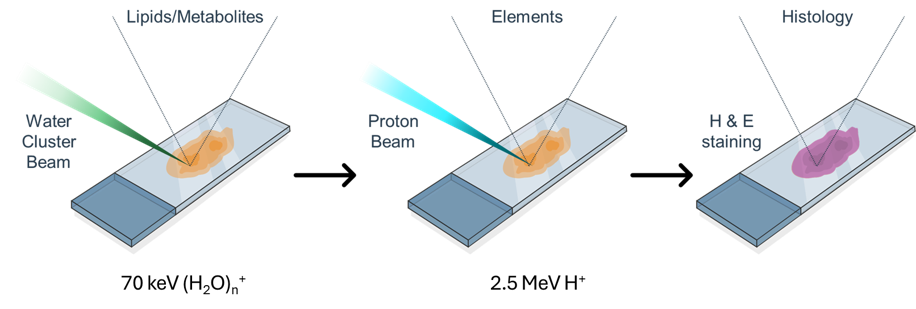
Why multimodal imaging?
We are developing analytical strategies to combine MeV ion beam elemental mapping with mass spectrometry imaging (MSI).
This will help to understand (e.g.) the impact of the below on the local chemistry (e.g. metabolites, proteins, lipids).
☐ Metal nanoparticles
☐ Elemental accumulation/depletion
☐ Metal containing drugs
But we want to perform sequential measurements on a single sample, because features are not always accurately reproduced in sequential sections.
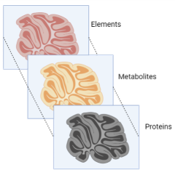
What are the challenges?
☐ Expertise and instrumentation are not normally co-located
☐ Different sample handling requirements
☐ Techniques are potentially destructive (what is the correct workflow?)
☐ Different data handling strategies
Multimodal Imaging: Elements & Molecules in Biological Samples
Catia Costa & Melanie J. Bailey


📰
Costa, C et al. Metabolites 2023, 13, 262.
DOI:https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020262

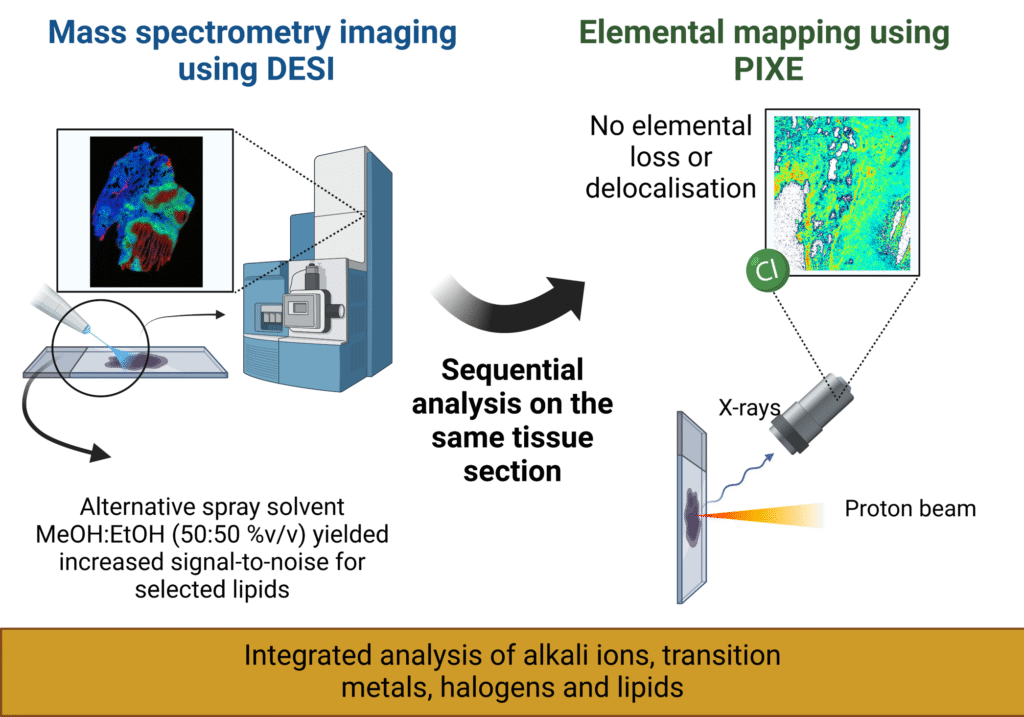
Desorption electrospray ionisation (DESI) and particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE)
☐ Using a spray solvent consisting of 50:50 (%v/v) methanol:ethanol enables sequential molecular (DESI) elemental (PIXE) mapping out on the same tissue section.
☐ This novel spray solvent mixture does not cause measurable loss or delocalisation of elemental signatures.
☐ This is desirable to allow accurate correlation of elemental and molecular features since regions of interest are not always accurately reproduced in sequential sections. In this work, the newsolvent system produced similar, if not better, lipid coverage and sensitivity in positive ion mode when compared to the conventional methanol:water solvent.

Time of Flight - Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis
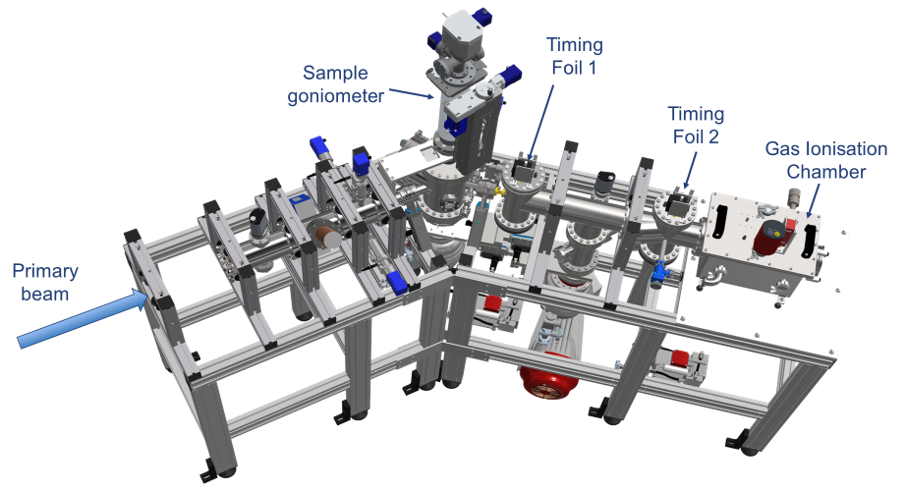
Time of Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA)
Matthew Sharpe & Callum McAleese


📰
Yifu Shi, et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023; 123 (26): 261106.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0174131
Desorption electrospray ionisation (DESI) and particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE)
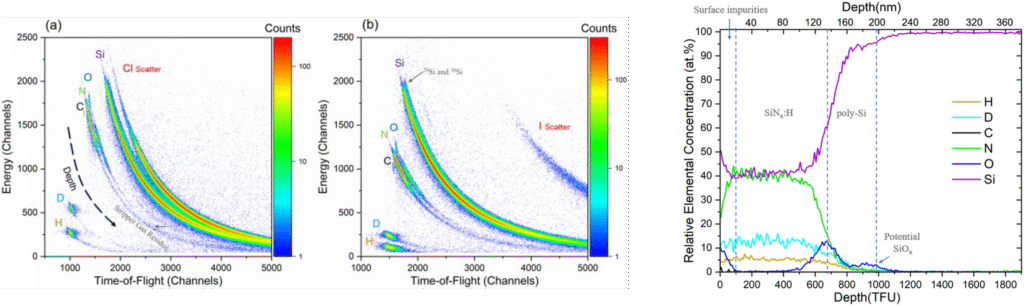
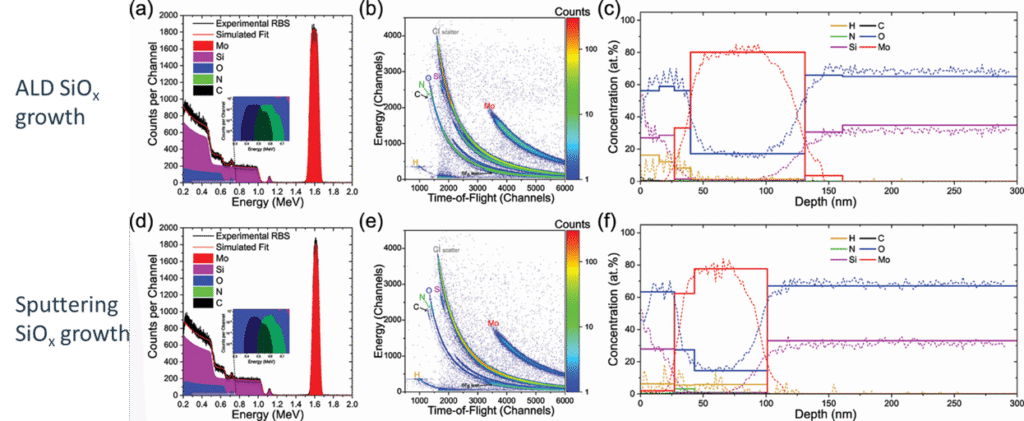
- The work investigates passivating‐contact stacks for solar cells; specifically thin film contact structures comprising e.g. poly-Si on SiOx.
- ToF-ERDA employed to directly detect and depth‐profile hydrogen (and deuterium) in these thin‐film stacks.
- The study shows that ToF-ERDA can resolve H/D. Artifact issues common to other techniques (e.g., SIMS) are mitigated by ToF-ERDA.
- Annealing treatments change the H/D distribution and that these changes correlate with passivation quality improvements. For example, H/D removal or redistribution is linked to changes in the interface oxide and poly‐Si structure.

Time of Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA)
Matthew Sharpe & Callum McAleese


📰
Björn Bonnet, et al. Environmental Science & Technology 2025 59 (4), 2222-2232.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.4c09474
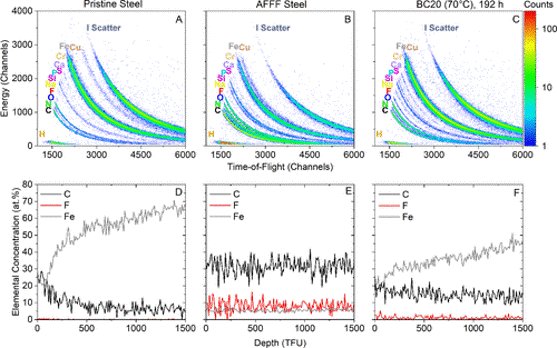
Decontamination and Surface Analysis of PFAS-Contaminated Fire Suppression System Pipes: Effects of Cleaning Agents and Temperature
- The work addresses decontamination of infrastructure surfaces (specifically stainless steel pipes) that are contaminated by firefighting foams containing Per‐ and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS).
- Time‐of‐Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA) is applied to analyse the pipe surfaces after different cleaning procedures. It enabled measurement of remaining fluorine (F) on the interior surfaces.
- ToF-ERDA results confirmed that even after cleaning there remained residual fluorine on the pipe surfaces (including deeper in the surface layers).
- The depth‐profiling capability of ToF-ERDA added critical insight about what’s left behind on surfaces.

Time of Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA)
Matthew Sharpe & Callum McAleese


📰
Shim, Hongjae et al. Joule, Volume 9, Issue 8, 102043
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2025.102043
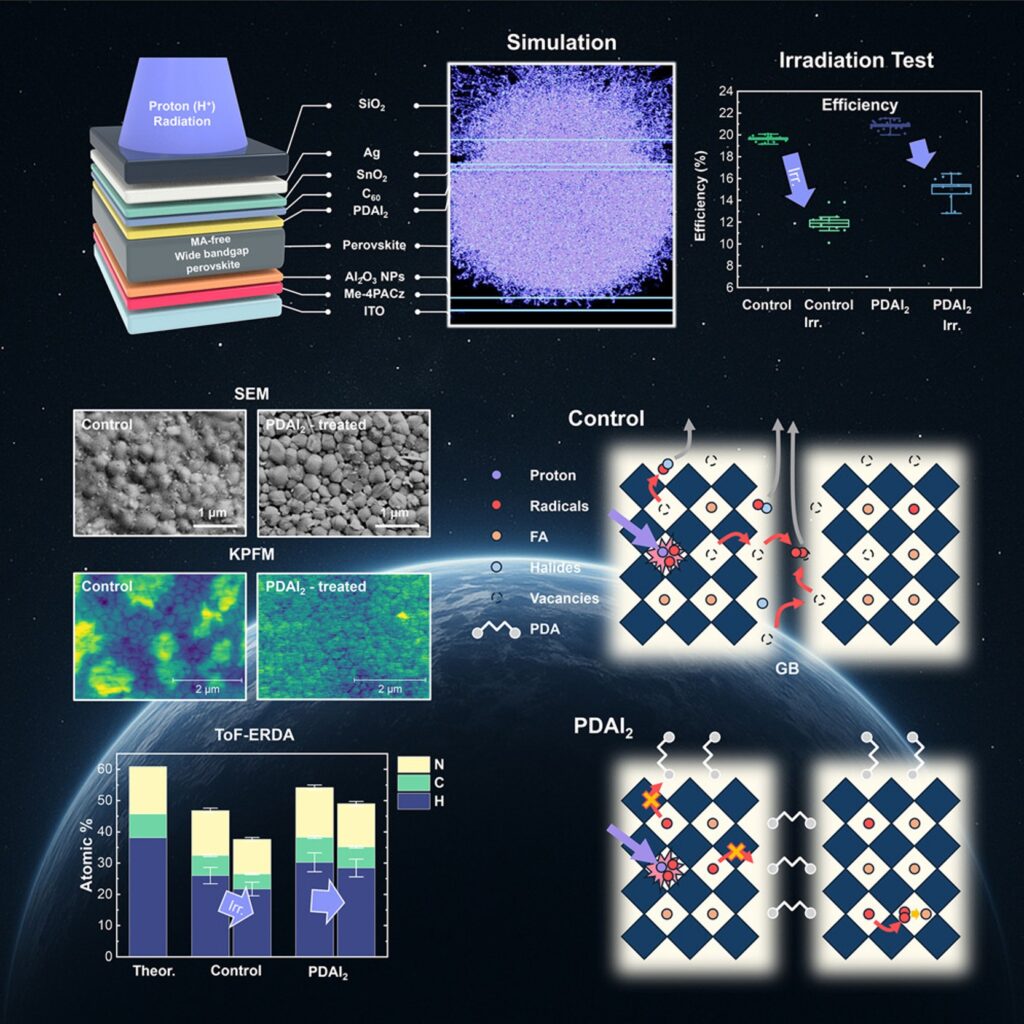
Perovskite solar cells for space applications
ToF-ERDA was used to quantitatively analyse elemental composition (especially light organic species such as H, C, N) and depth profiles in the perovskite layers before and after proton irradiation.
ToF-ERDA played a central diagnostic role in this work, enabling:
- Accurate quantification of elemental loss (H, C, N) due to irradiation;
- Verification that PDAI₂ mitigates organic volatilisation;
- Support for the proposed mechanism of radiation-induced defect passivation and lattice stabilization.

Time of Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA)
Matthew Sharpe & Callum McAleese


📰
Connor Beer, et al. Acta Materialia, 298, 2025, 121391.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2025.121391.
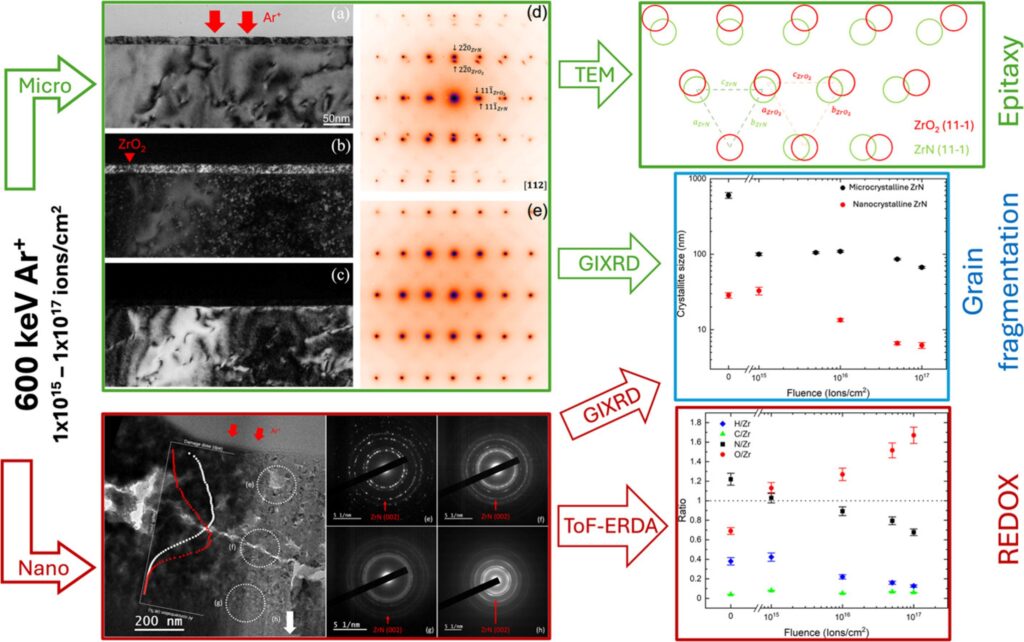
Radiation effects on nuclear surrogate material
- Micro‐crystalline vs nano‐crystalline ZrN (zirconium nitride) thin films respond to radiation (ion beam or other irradiation) in terms of structural and compositional changes.
- The study applied ToF-ERDA to probe changes in elemental composition (particularly light elements like O, N) and depth distribution caused by radiation in the films.
- The findings suggest that nano‐crystalline ZrN is more susceptible to oxidation under irradiation than the micro‐crystalline form, and that the distribution of oxygen and nitrogen evolves differently in both forms.

Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry
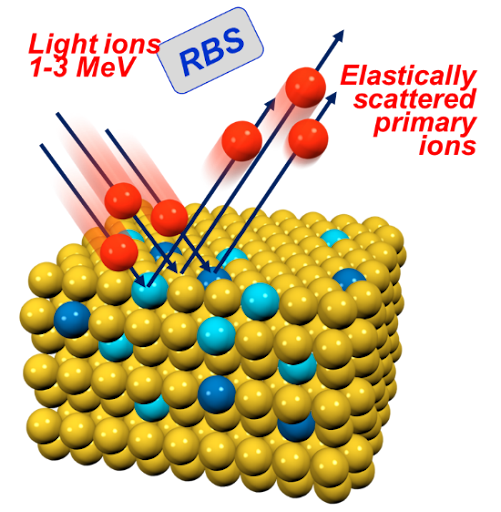
Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used to determine the composition and structure of materials by measuring how high-energy ions scatter off a sample. In a typical RBS experiment, a beam of energetic ions—usually helium ions—is directed at the material. When these ions collide with atoms in the sample, some scatter backward at high angles. By detecting these backscattered ions and measuring their energies, researchers can infer the mass and depth of the atoms they interacted with. Heavier atoms scatter ions more strongly and produce higher-energy signals, allowing clear identification of elements.

Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry
Matthew Sharpe


📰
H. R. J. Cox, et . Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2408437.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202408437
The Role of Hydrogen in ReRAM
- RBS is used to measure heavier elements in the sample, giving the thicknesses, compositions and interface demarcations of the device layers. RBS allows determination of major elemental changes and detection of any significant intermixing or diffusion of heavier species due to device operation or hydrogen impact.
- ToF-ERDA is crucial for detecting and quantifying light elements, especially hydrogen and other light atomic species (e.g., O, N) within the device layers.

Time of Flight Elastic Recoil Detection Analysis (ToF-ERDA)
Matthew Sharpe


📰
M. K. Sharpe, et al. J. Appl. Phys. 2019; 126 (12): 125706.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5109653
RBS channelling: A comparative study of epitaxial InGaAsBi/InP structures
The work uses RBS channelling to investigate the crystallographic quality, defect structure, and damage (or implantation-induced changes) in a material (InGaAsBi/InP structures) following some processing or irradiation.
Through channelling measurements:
Determine the fraction of atoms displaced from lattice sites.
Identify damage depth profiles.
Assess the recovery/annealing behaviour of the structure.
This work links the degree of lattice disorder (using RBS channelling) to material performance (e.g., electrical, optical or mechanical) or to how growth conditions affect structural integrity.

Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
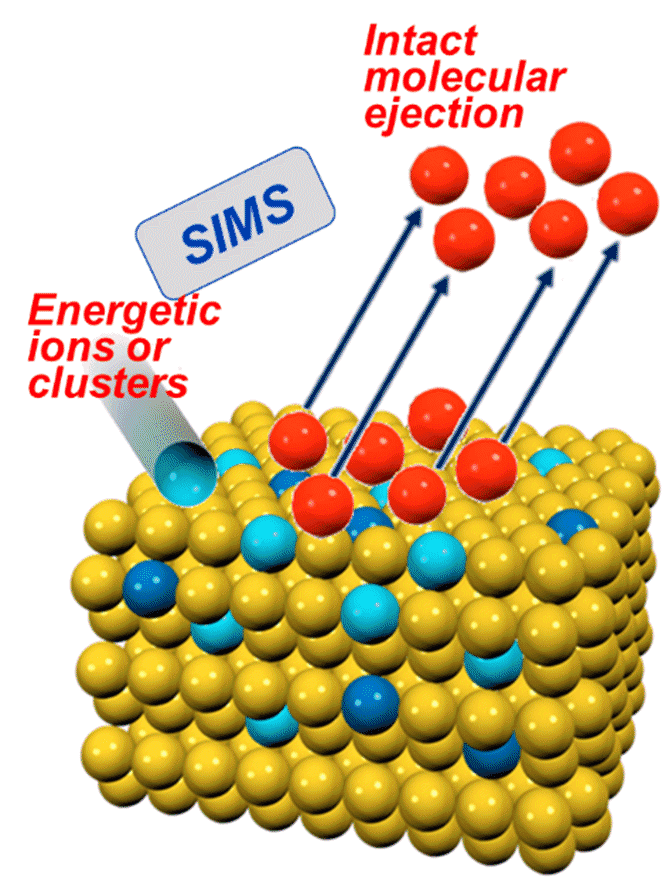
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) is an analytical technique that uses a focused primary ion beam to sputter atoms and molecules from a sample’s surface, generating secondary ions that are then analyzed by a mass spectrometer. It offers extremely high surface sensitivity, capable of detecting elements at ppm–ppb levels, and allows depth profiling by continuously sputtering deeper layers while monitoring composition. In ion beam research, SIMS is crucial for studying ion–solid interactions, sputtering yields, damage mechanisms, and implantation effects. It also aids in understanding how ions redistribute or activate within materials during ion beam processing.
Multimodal Imaging: Elements & Molecules in Biological Samples
Catia Costa & Melanie J. Bailey


📰
Catia Costa, et al. Analytical Chemistry 2025 97 (30), 16573-16582
DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c02890

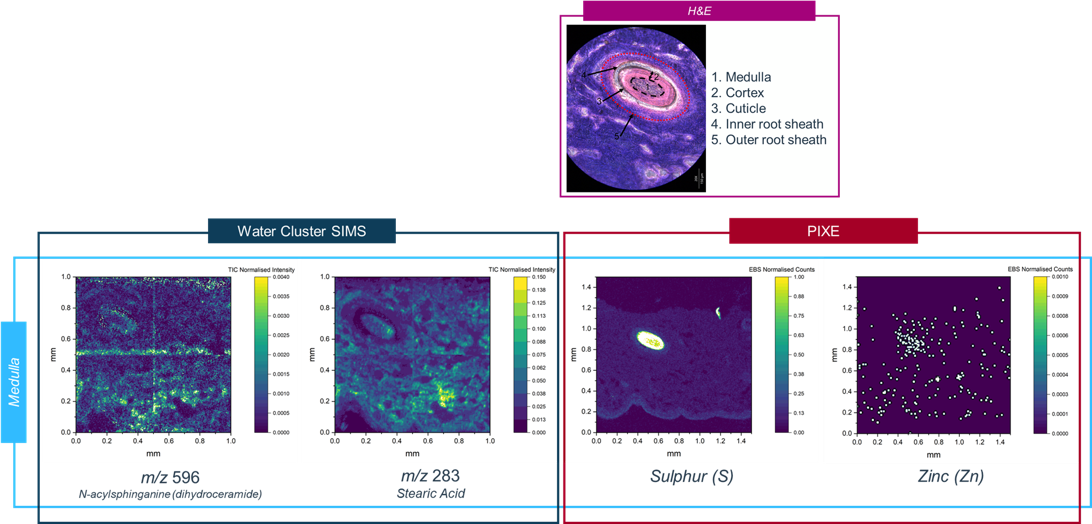
Secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) and particle induced X-ray emission (PIXE)
- Developed a workflow that can be applied to biological tissues/cells for multimodal elemental and molecular imaging at the micron scale using keV and MeV ion beams on the same sample
- This work opens up the exciting prospect of colocalizing metals or other elements with metabolites and lipids in biological systems below the single cell level, and future work will need to explore how to deal with the difference in information depths
Multimodal Imaging: Elements & Molecules in Biological Samples
Catia Costa & Melanie J. Bailey



Multimodal ion beam imaging facility EPSRC grant EP/Y015134/1
The proposed new system will incorporate a design where the quality of the mass spectrometry is independent of the nature of the primary ion beam used, and will capitalise on the optimised sample handling, ion transmission and data handling of the commercialised keV SIMS system. The addition of the MeV ion beam into the system is unprecedented internationally and will be provided by the existing tandem accelerator at the SIBC.
System will include:
- Focussed MeV ion beam for conventional IBA and MeV-SIMS
- Water cluster (keV) primary ion beam
- C60 (kV) primary ion beam
- TOF analyser for keV and MeV-SIMS experiments
- X-ray and particle detectors for conventional IBA
When installed and commissioned (early 2026), the system will allow:
- Elemental imaging (IBA)
- Depth profiling (IBA)
- 3D imaging of small and large molecules (keV and MeV-SIMS)
- Multimodal imaging of elemental and molecular species (SIMS and IBA)
- Multimodal depth profiling (SIMS and IBA)
Ion Implantation & Irradiation
Ion implantation and irradiation are key techniques in ion beam research, used to modify the structural, electronic, magnetic, and chemical properties of materials with high precision. In ion implantation, energetic ions are accelerated and directed into a target, allowing controlled introduction of dopants or defects at specific depths determined by ion energy and mass. This process is fundamental in semiconductor device fabrication, where dopants such as boron or phosphorus are implanted to tailor electrical conductivity. Ion irradiation, on the other hand, focuses on altering materials by generating defects, phase transformations, or microstructural changes through controlled ion-material interactions. These interactions can produce phenomena such as defect engineering, amorphization, nano-pattern formation, or radiation hardening. Both processes rely on ion beam parameters—including energy, fluence, species, and flux—to tune modification levels with nanometer-scale accuracy.

Ion Implantation & Irradiation
Ella Schneider


📰
Ella Schneider and Jonathan England; ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2023 15 (17), 21609-21617 DOI: 10.1021/acsami.3c01112
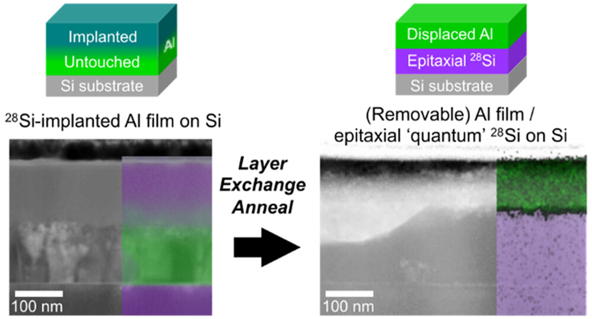
Isotopically Enriched Layers for Quantum Computers Formed by 28Si Implantation and Layer Exchange
The scale of the problem
- 28Si enrichment is crucial for production of group IV semiconductor-based quantum computers. Cryogenically cooled, monocrystalline 28Si is a spin-free, vacuum-like environment where qubits are protected from sources of decoherence that cause loss of quantum information.
- Currently, 28Si enrichment techniques rely on deposition of centrifuged SiF4 gas, the source of which is not widely available, or bespoke ion implantation methods. Previously, conventional ion implantation into naturalSi substrates has produced heavily oxidized 28Si layers.
- Here we report on a novel enrichment process involving ion implantation of 28Si into Al films deposited on native-oxide free Si substrates followed by layer exchange crystallization. We measured continuous, oxygen-free epitaxial 28Si enriched to 99.7%. Increases in isotopic enrichment are possible, and improvements in crystal quality, aluminum content, and thickness uniformity are required before the process can be considered viable.
- Required implant fluences are an order of magnitude lower than those required for enrichment by direct 28Si implants into Si and can be chosen to control the final thickness of the enriched layer. We show that implanted layer exchange could potentially produce quantum grade 28Si using conventional semiconductor foundry equipment within production-worthy time scales.

Deterministic Implantation
Deterministic implantation is an advanced ion beam technique that enables the placement of individual ions at precisely defined locations, offering single-ion control that surpasses conventional implantation methods. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on statistical ion delivery, deterministic implantation uses real-time ion detection systems—such as secondary electron emission or ion-induced charge signals—to confirm the arrival of each ion before allowing the next one to be implanted. This method is crucial for applications requiring atomic-scale accuracy, including the fabrication of quantum devices, single-atom transistors, and defect-based qubits in materials like silicon, diamond, or silicon carbide. By synchronizing ion delivery with detection, deterministic implantation ensures accurate ion count, spatial precision, and minimal damage to the surrounding lattice.
Deterministic Implantation
Ella Schneider


📰
Preprint: Ella B Schneider, et al. 2025; arXiv:2510.14495 https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.14495
Submitted to Nano Letters
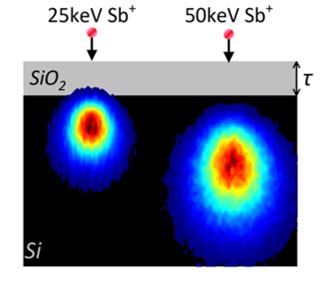
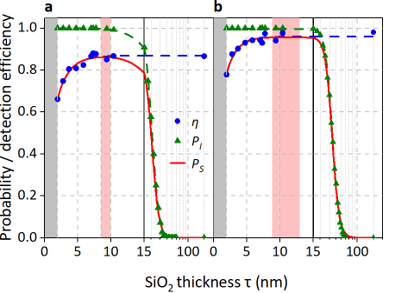
Enhanced Secondary Electron Detection of Single Ion Implants in Silicon Through Thin SiO2 Layers
- Deterministic placement of single dopants is essential for scalable quantum devices based on group-V donors in silicon.
- Using the single ion multispecies positioning at low energy (SIMPLE) tool, we demonstrate a non-destructive, high-efficiency method for detecting individual ion implantation events using secondary electrons (SEs)
- Using low-energy Sb ions implanted into undoped silicon, we achieve up to 98% single-ion detection efficiency, verified by calibrated ion-current measurements before and after implantation.
- We find that introducing a controlled SiO2 capping layer significantly enhances SE yield, consistent with an increased electron mean free path in the oxide, while maintaining high probability of successful ion deposition in the underlying substrate.